Peppermint OS is a Linux distribution based on Debian and Devuan Stable (originally based on Ubuntu). The desktop environment it utilizes is Xfce, which is customizable and lightweight. With relatively few hardware resources needed to run Peppermint, it attempts to give beginners a friendly Linux atmosphere.
Peppermint OS places emphasis on speed, ease of use, and interaction with cloud-based technologies, standing out among lightweight and user-friendly Linux distributions. For those who want a fast and efficient computing experience, this is a great option.
In addition, it gives users the flexibility to customize the system to suit their requirements. Besides that, it is suitable for both beginners and seasoned users because it blends a modern feature set with a minimalistic design.
Peppermint OS Is Now Based on Debian 12
On July 1, 2023, the Peppermint OS team released fresh ISO images based on the Debian GNU/Linux 12 “Bookworm” operating system, generally available for download.
This latest Peppermint OS version ships with new branding, a new style for the Plymouth boot splash screen, new Marawaita themes, and new Tela icons, among other enhancements and updated artwork.
In addition, Kumo now employs the Lua programming language and has a simpler GUI; the neofetch was modified to use the basic output without a logo; and the Welcome screen and Peppermint Hub have been updated to remove or add new features based on user feedback.
On top of that, the Calamares graphical installer is also included in this new release, and the documentation is updated. To upgrade from Peppermint, which is based on Debian GNU/Linux 11 “Bullseye“, to Debian GNU/Linux 12 “Bookworm“, you can use Debian’s upgrade process, which entails modifying the repositories to point to Bookworm.
Peppermint OS Review
Here is an overview of Peppermint OS.
Peppermint OS – Look and Feel
The welcome screen is the first graphical interface a user sees when they boot into Peppermint OS. Users can select their language, location, and keyboard layout and access several helpful tools and features from the welcome screen.
Additionally, the welcome screen detects the operating system base-Debian or Devuan, and shows the relevant information and logo.
Peppermint’s welcome screen is designed to be simple, aesthetically pleasing, and easy to use. It features a bright banner at the top and a peppermint logo on a dark backdrop. The operating system’s version number and codename, such as Peppermint 12 “Bookworm” are displayed in the banner.
Although Peppermint OS releases and upgrades may bring about changes to its look and content, its major goal is still to make the onboarding process easier for users.
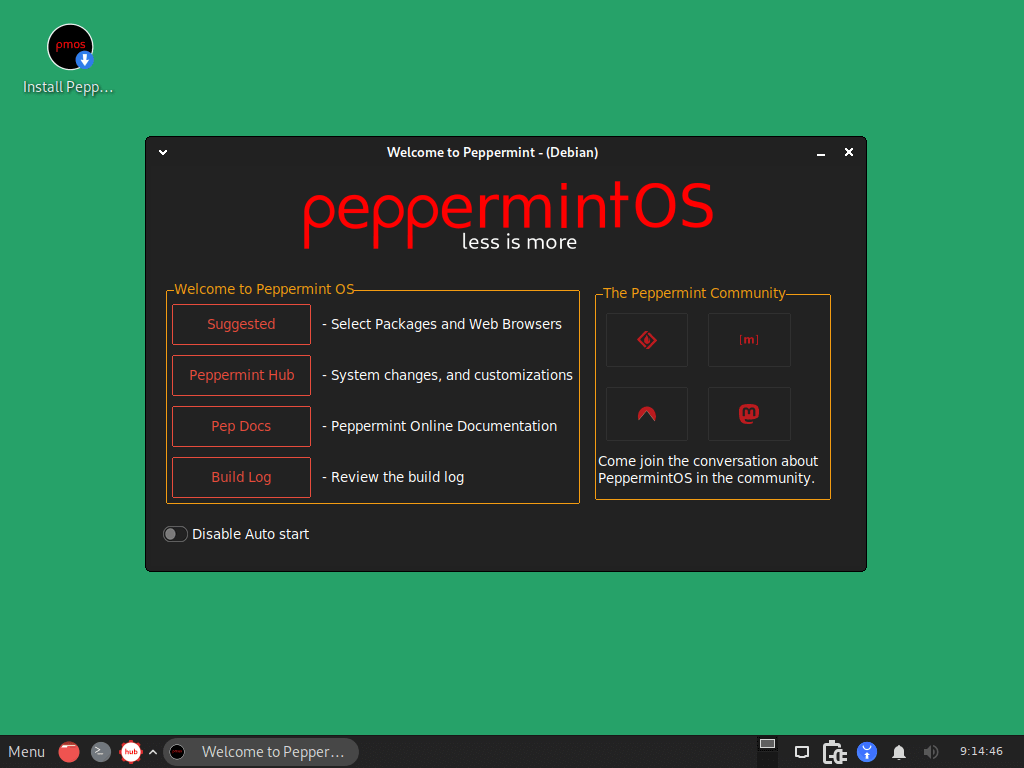
Peppermint Hub
Peppermint Hub serves as a central location for accessing different system management tools and settings. It integrates all of the features from the control center and previous settings into a single, practical interface.
With Peppermint Hub, you can:
- Install programs from third-party or official repositories.
- Personalize your system’s look, feel, network, power, and other features.
- Visit the help center to access tutorials, forums, support channels, and documentation about your system.
- Check the system’s basic details, including the license, base, desktop environment, and kernel version.
Tkinter GUI Platform
The Tkinter GUI platform is a tool that lets you utilize the Tkinter module, which is a standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit, to construct graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for your Python programs.
The Tkinter GUI platform can be accessed via Peppermint Hub. With the Tkinter GUI platform, you can use Bootstrap—a renowned framework for creating mobile-first and responsive websites—to design and alter your GUIs.
TTK Creator is another tool that you can use to generate and apply Tkinter themes to your graphical user interfaces. Additionally, the Tkinter GUI platform offers you various Tkinter GUI templates and samples that you can use as a guide or customize to your specifications.
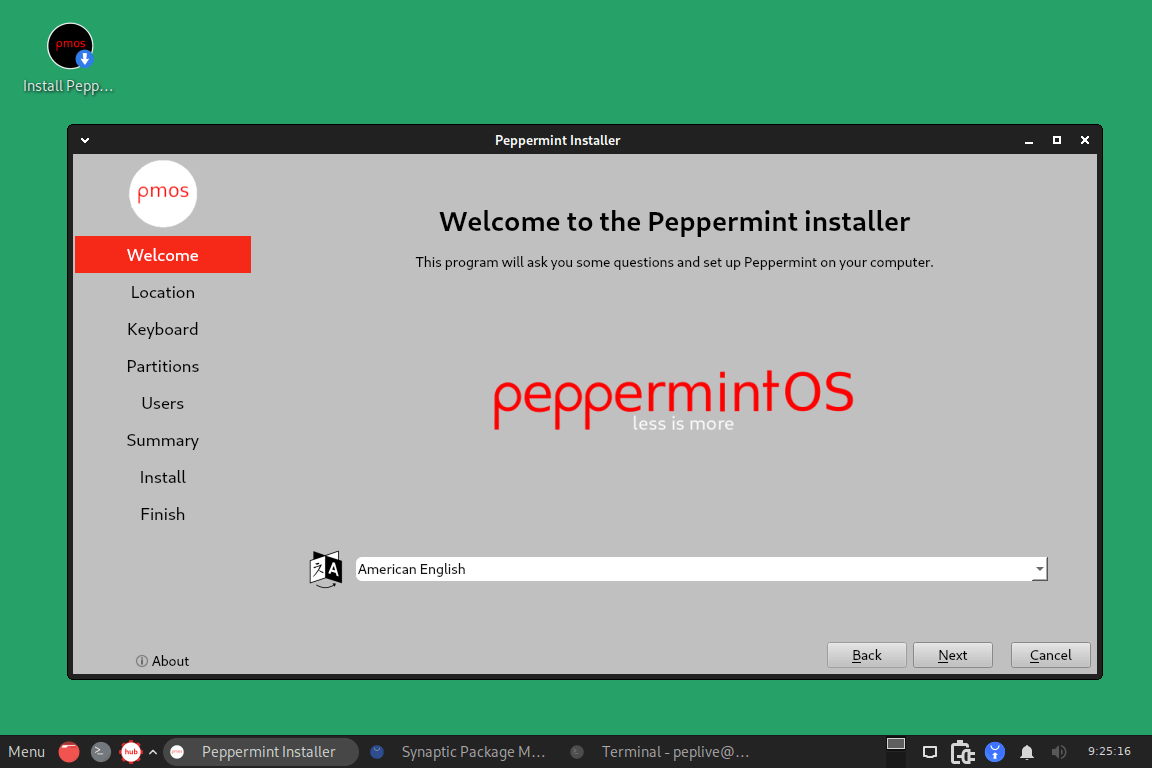
Calamares Installer
Most Linux distributions, including Peppermint OS, employ a graphical system installer, Calamares Installer, which offers an easy-to-use interface for users to configure the operating system on their computers, making the installation procedure simpler for them.
The Calamares Installer plays a vital part in the Peppermint OS installation, as it provides an easy-to-use and effective way to install the operating system on a variety of hardware setups. Users’ installation processes run more smoothly because of its user-friendly interface and step-by-step instructions.
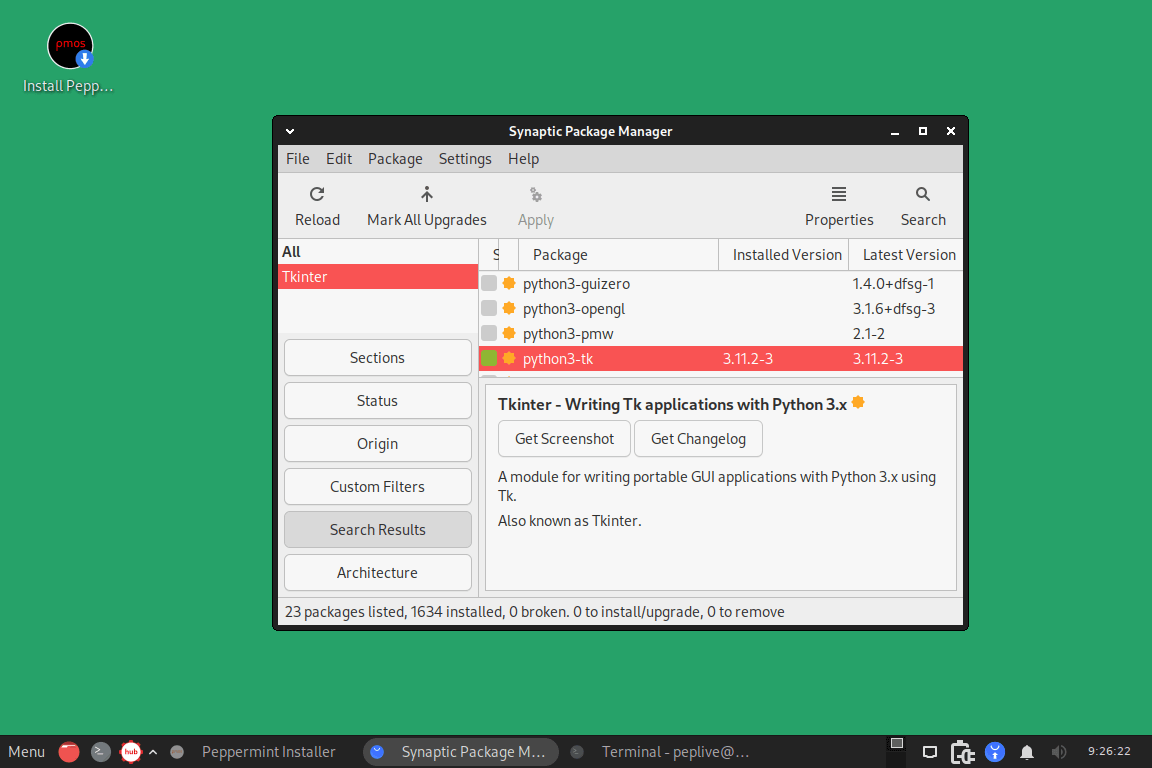
Synaptic Package Manager
On your Peppermint OS, you can install, uninstall, and manage software packages using Synaptic, a graphical package management application.
Synaptic directly impacts the system; always exercise caution when using it, especially when installing or deleting packages. To prevent inadvertent system modifications, always make sure you are familiar with the packages you are adding, deleting, or altering.
Kumo SSB
Kumo SSB is an integrated feature of Peppermint OS that enables users to develop site-specific browsers (SSBs) for their preferred online apps.
Compared to using a standard web browser, these SSBs provide a more concentrated and app-like experience by serving as isolated, dedicated instances for particular web services.
Email, social media, streaming, gaming, and other web-based applications can all benefit from a more concentrated and engaging user experience from SSBs.
Kumo SSB has been completely redesigned from the Ubuntu-based Ice, the previous SSB tool. Aside from being a tool for creating launchers, Kumo SSB now functions more like an SSB launcher.
Thunar File Manager
Thunar is an essential component of the Xfce desktop environment, which is a lightweight file manager renowned for its ease of use, speed, and effectiveness. It is the default file manager in Peppermint OS.
Among the features it packs are:
- Users can quickly navigate through their files and folders thanks to the intuitive interface it offers.
- It can copy, move, rename, and delete files, as well as directories.
- Thunar comes with a bulk renaming tool that lets users rename several files in a personalized or sequential way.
- It comes with built-in capabilities that allow users to access mounted filesystems and network shares.
- To give users a visual representation of the files in the file manager, Thunar creates thumbnail previews for a variety of file formats.
- Through plugins, users can add capabilities like archive management, unique actions, and more context menu options to Thunar, thereby expanding its capabilities.
xDaily – System Maintenance Tool
The latest release of Peppermint OS features xDaily, which is simply a tool that can assist you in manually checking for updates, optimizing your system, and resolving possible issues. The Peppermint Hub, which is a central location for managing your system tools and settings, provides access to xDaily.
To get started with xDaily, navigate through the Peppermint Hub and search for the xDaily button. With just one click, a terminal window will launch and request that you enter your password.
After that, a menu with several options will appear, including:
- Update System – with this option, you can install any updates that are available for your system from third-party or official repositories.
- Clean System – with this option, you will get rid of any files that aren’t needed and could slow down your system, like temporary files, logs, and cache.
- Fix System – with this option, you can resolve any typical issues that could arise with your system, like corrupted files, missing dependencies, or broken packages.
By selecting the requested option and hitting Enter, xDaily will carry out the action you selected and provide the outcomes and progress to you.
hBlock – Tracker Blocking Tool
hBlock is a lightweight and efficient ad and tracker-blocking tool that uses the /etc/hosts file to stop your system from loading content from recognized tracking and advertising domains by rerouting them to a local address (usually 0.0.0.0 or 127.0.0.1).
To keep your system safe from fresh threats of unwanted information, hBlock can be configured to automatically update the host file with the latest listings of ad and tracker domains. To customize the blocking behavior, users can add or remove specific domains from the blocklist.
To install hBlock, use the command-line utility or the package manager as shown.
sudo apt update sudo apt install hblock
Through the integration of hBlock into Peppermint OS, you can leverage its ad-blocking features to enhance your online privacy and browsing experience.
Cloud Integration
Users can use online services like Gmail, Google Drive, and others straight from the system menu thanks to its seamless integration of cloud and web-based applications into the desktop environment. Through this integration, local and internet resources are more easily accessed, increasing productivity.
Themes, Icons, and Tweaks
Pre-installed themes in Peppermint OS usually allow you to customize the desktop’s appearance. To modify window borders, controls, and icon styles, users can flip between these themes. Navigating to the appearance settings inside the system menu is typically required to access these themes.
In addition, Peppermint OS offers the possibility to modify the set of icons used across the system, much like themes. This may change how icons display on the desktop, in different application menus, and in the file manager. Usually, users can choose from a variety of icon sets via the system settings.
You can also add additional customization to Peppermint OS by using tweak tools made for LXDE or GTK-based environments and installing third-party themes.
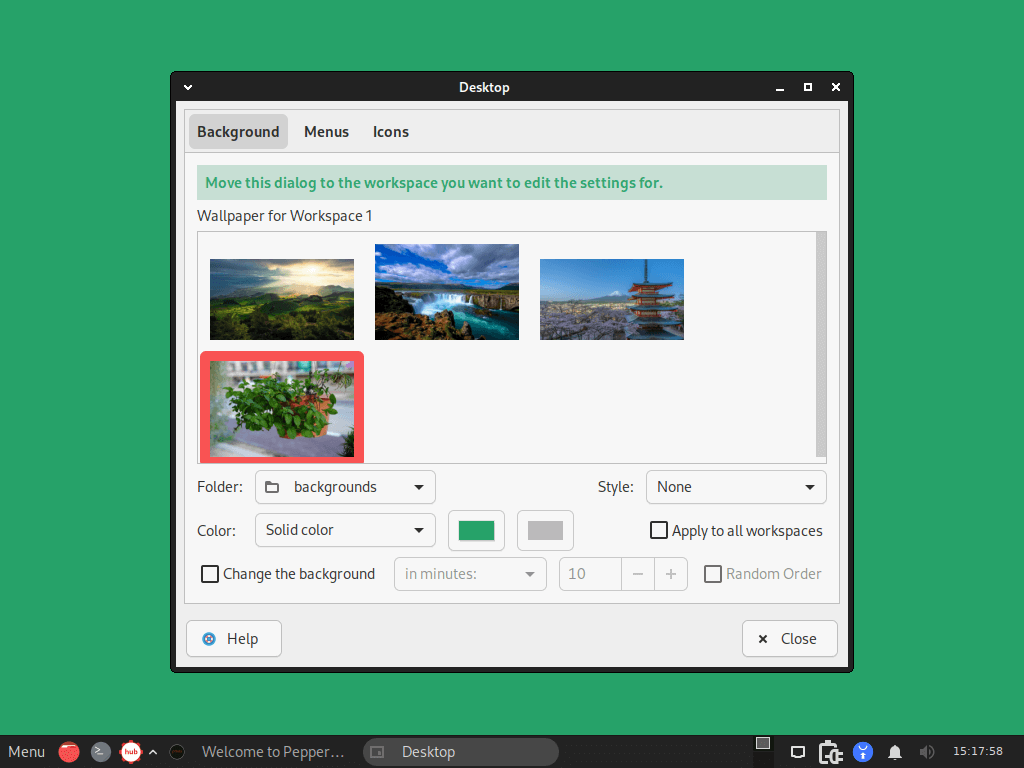
Desktop Wallpapers
Peppermint OS features a library of impeccable wallpapers. To get started, simply right-click on the desktop and select “Change Wallpaper” This makes it easy for users to change the desktop background.
In addition, the wallpapers come pre-installed on Peppermint OS, and users can also add their own images.
Community and Support
Users can interact with one another, ask for assistance, and exchange experiences through the community forums that Peppermint OS hosts. These forums are an invaluable tool for discussing features, fixing problems, and gaining guidance from knowledgeable developers and users.
Although the Peppermint OS community may not be as large or well-known as those of other larger Linux distributions, it is ultimately a close-knit group of people dedicated to helping one another, exchanging expertise, and working together to enhance the Peppermint OS experience as a whole.
Install Peppermint OS on Your System
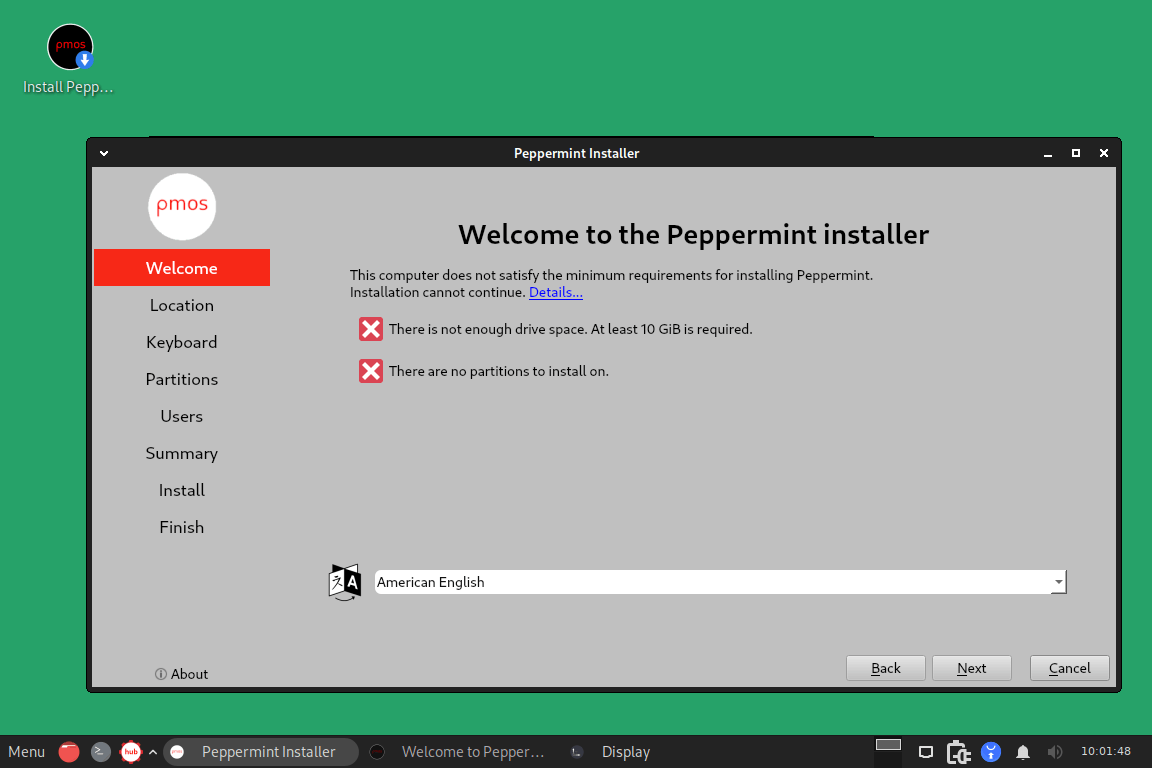
To install Peppermint OS, ensure your machine meets the following minimum requirements:
- 1GB RAM
- 10GB of hard drive space
- Processor based on Intel x86 architecture
To get started, head over to the official Peppermint OS download page and click the Download button to select your preferred ISO image based on your architecture.
Once the ISO file has been downloaded to your machine, you can use USB creator tools to create an installation medium with a USB drive and boot.
You’ll see a boot screen that presents several options to choose from. Select the default option and press Enter.
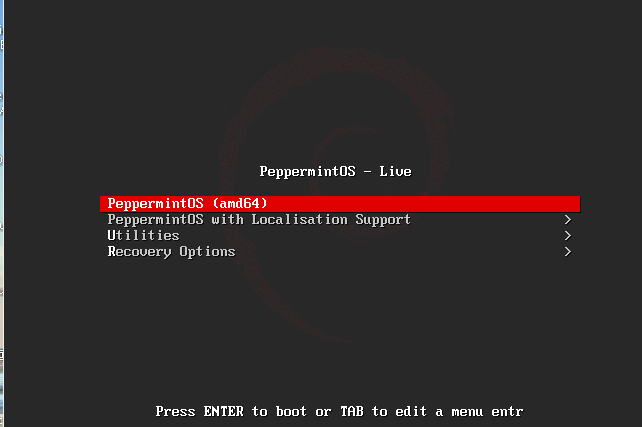
In this window, click the Install Peppermint OS tab on the top right of the welcome screen to start the installation.
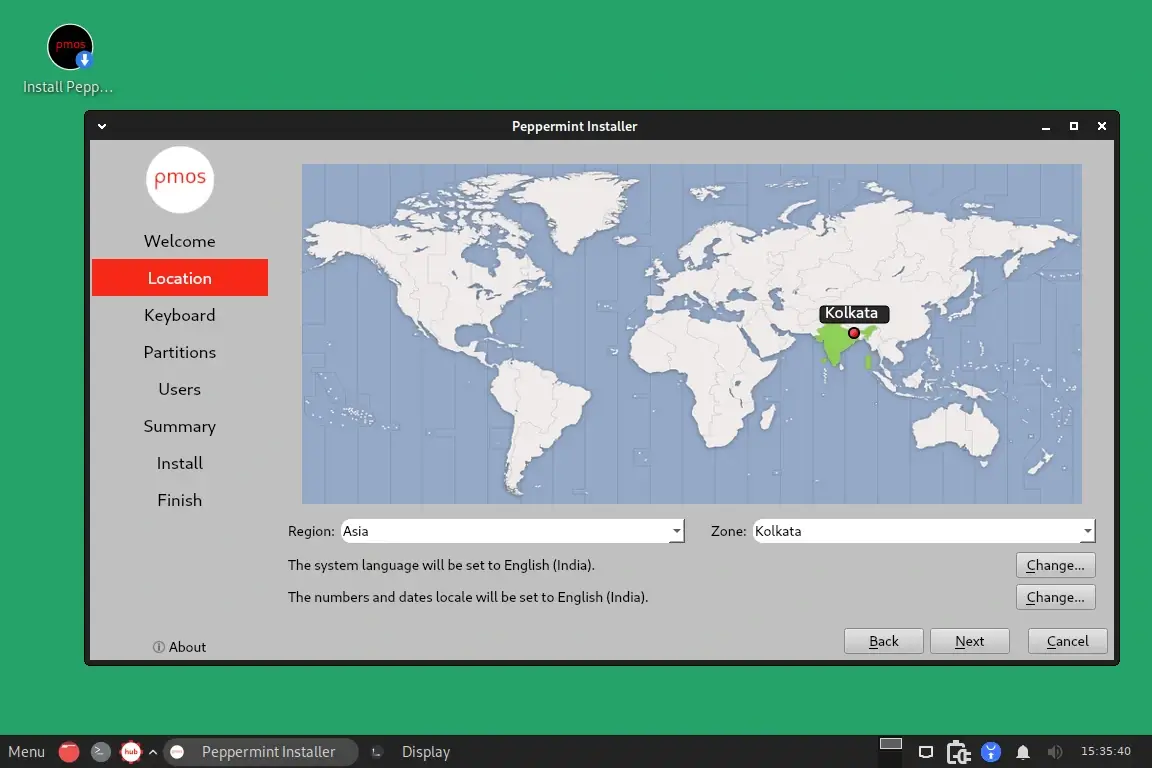
From here, select your preferred language and location.
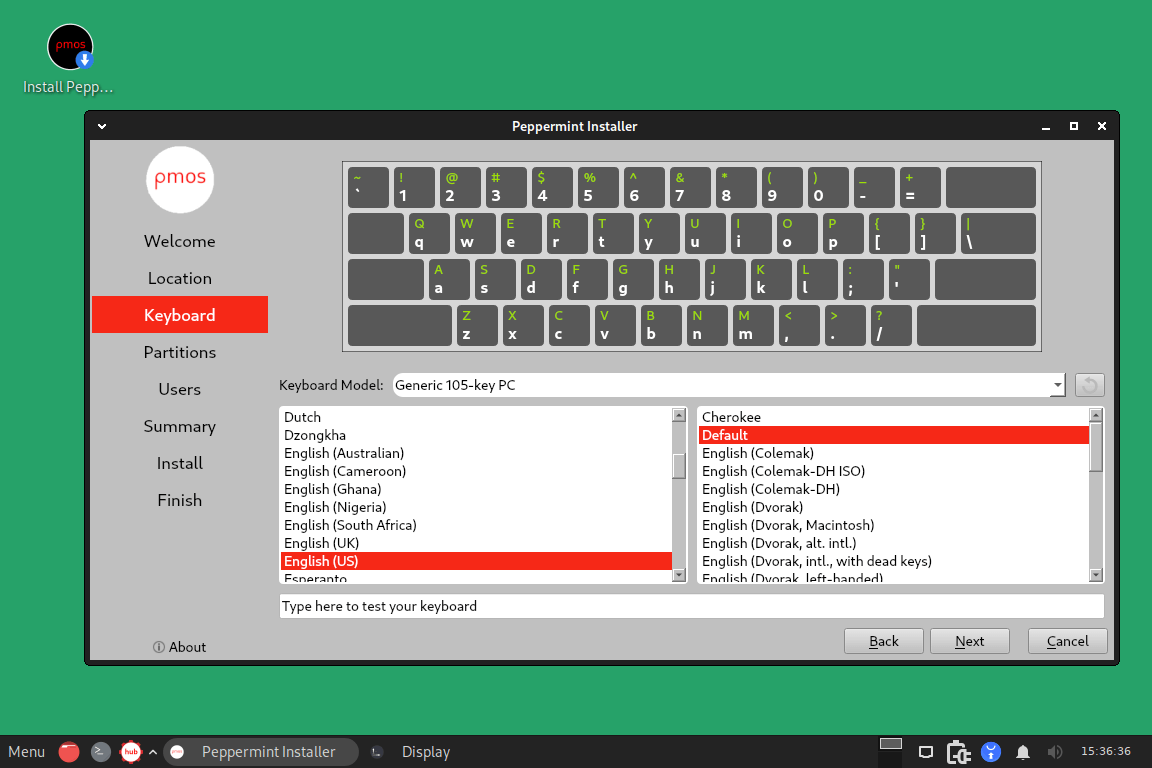
On the next screen, select your preferred keyboard layout.
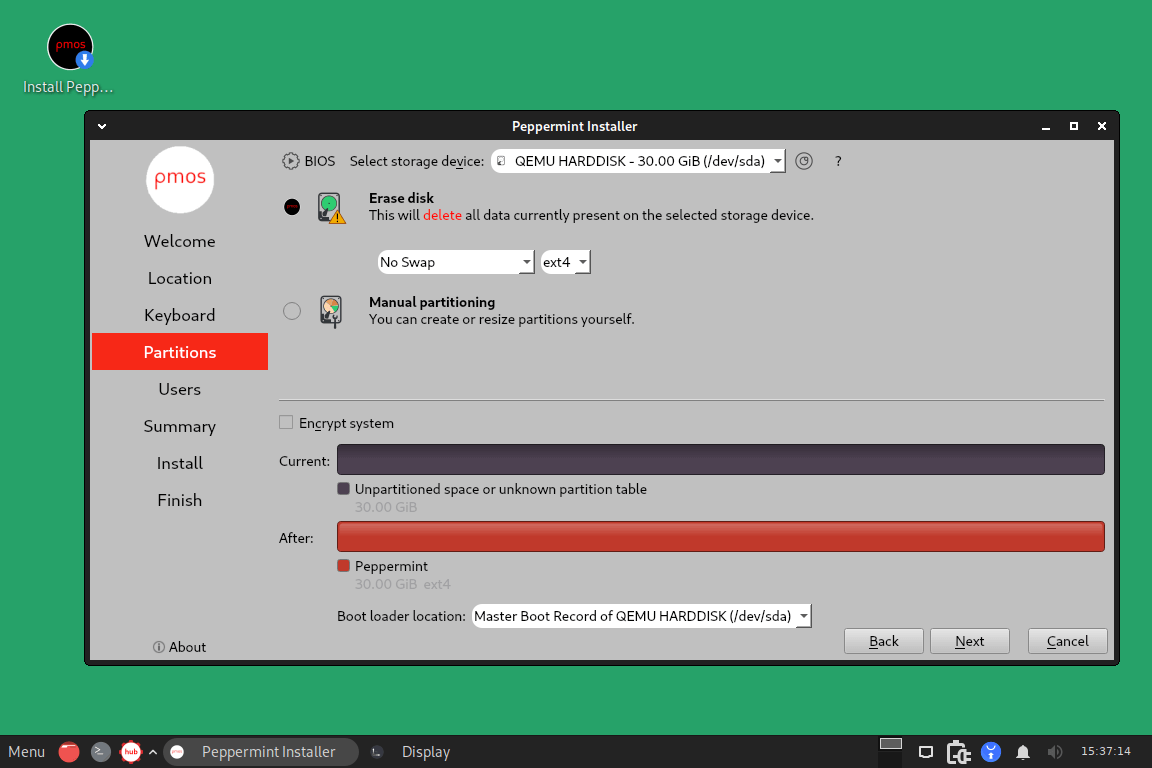
Here, click the Erase disk option (recommended for Linux beginners).
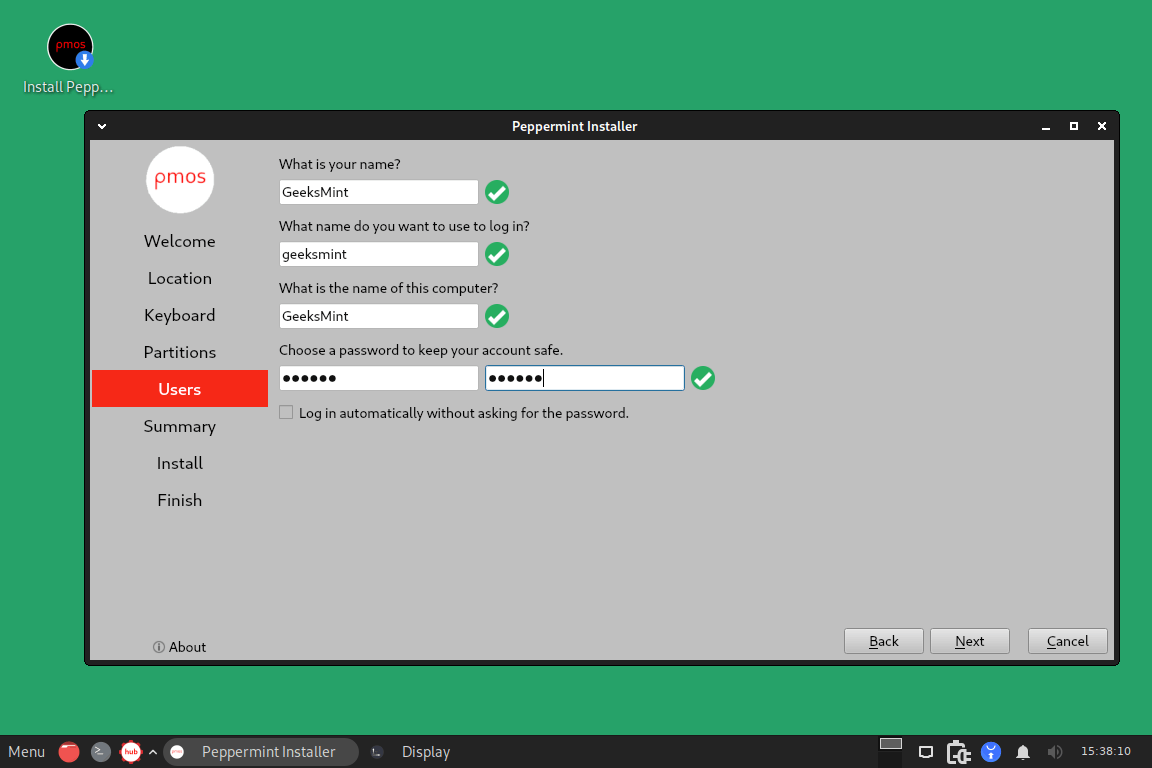
Use the UI on this screen to set a password, a username, and a name for your computer.
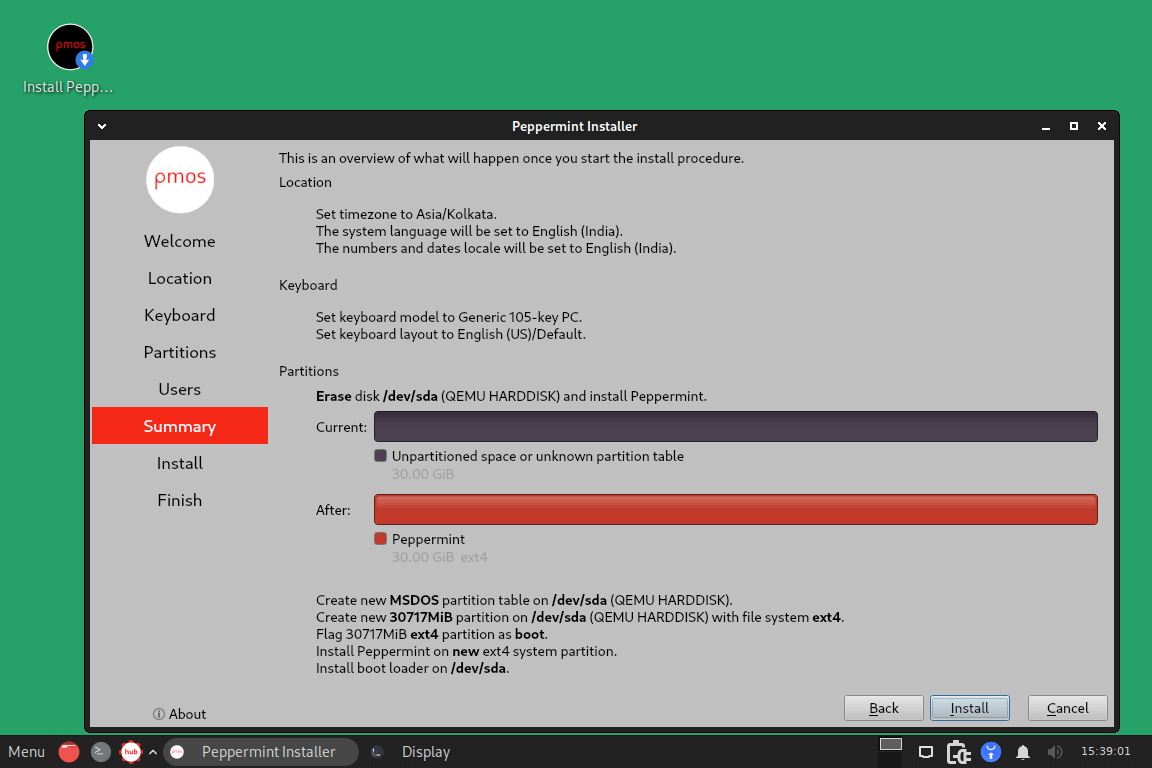
On this screen, you’ll be presented with an overview of what you want to install, crosscheck, and click the install button.
The Peppermint installation starts instantly; sit back and allow the installer to set up your OS.
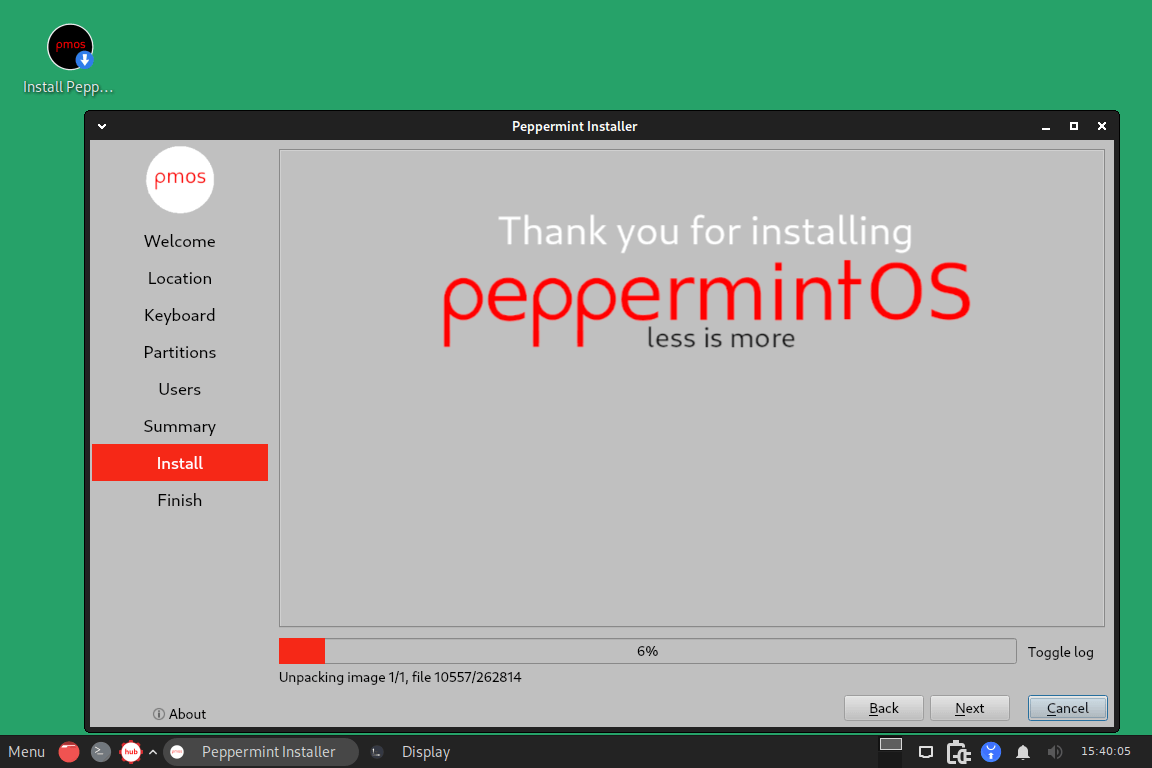
When the installation is done, click restart now in order to reboot the freshly installed OS.
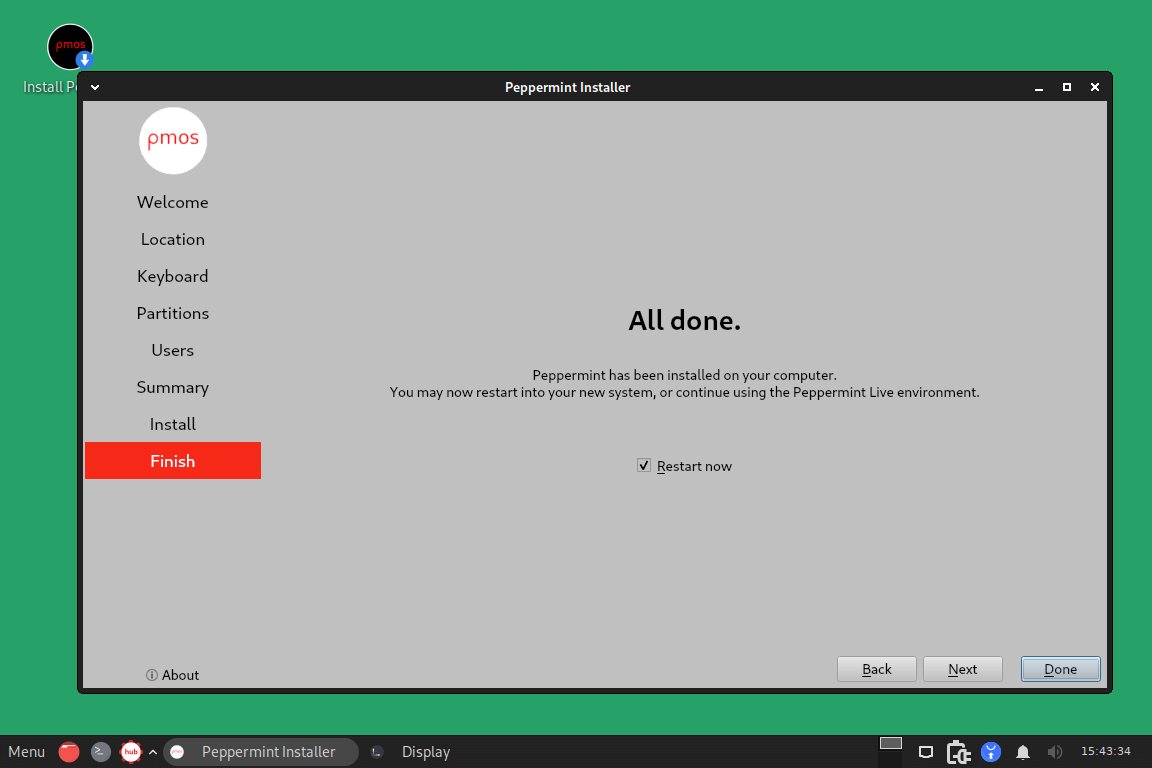
Peppermint should now be successfully installed on your computer after the installation is finished. To begin exploring and testing the OS applications, simply log in.
Conclusion
This concludes our comprehensive overview and installation of Peppermint OS, have fun using the distribution. Which feature amazes you about peppermint? Let me know in the comment section below.

An interesting Linux distribution project. Keep us posted